Brain
- Reporter 21
- 23 Oct, 2021
The brain is a complex and remarkable organ that serves as the control center of the human body. It is responsible for a wide range of functions, including cognitive processes, sensory perception, motor control, and regulating bodily functions. Here are some key aspects and functions of the brain:
Anatomy: The human brain is located within the skull and is divided into several major regions, including the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and diencephalon. The cerebrum, with its highly folded surface (cerebral cortex), is the largest and most prominent part of the brain and is responsible for higher-level functions such as thinking, memory, language, and conscious awareness.
Hemispheres: The brain is divided into two hemispheres, the right and left, each of which is associated with different functions. The left hemisphere is often considered dominant for language and analytical tasks, while the right hemisphere is involved in spatial perception and creativity.
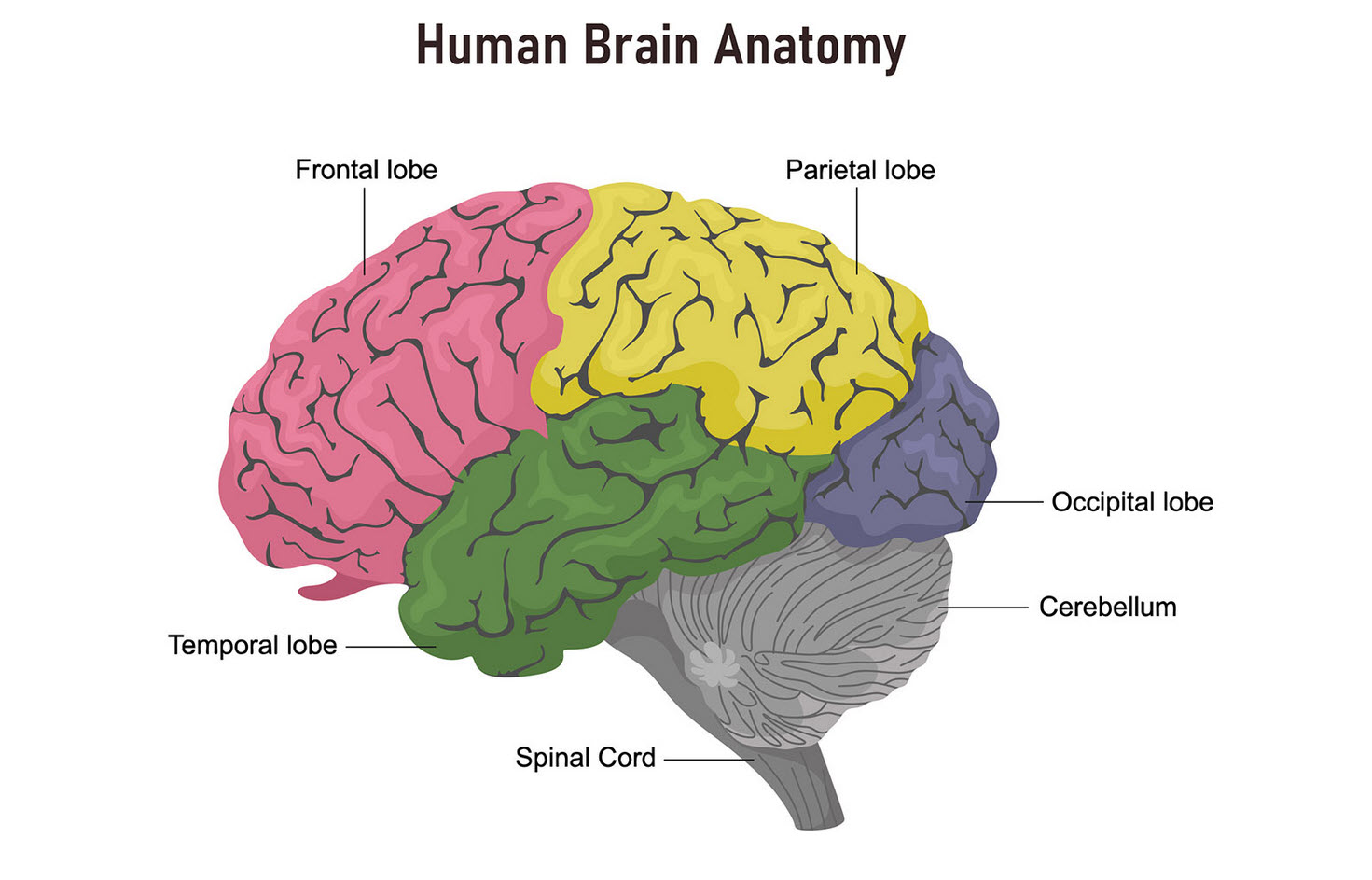
Cerebral Cortex: The cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the cerebrum and is responsible for many of the brain's cognitive functions. It is divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital, each with specific roles related to motor control, sensory processing, language, and more.
Neurons: Neurons, or nerve cells, are the building blocks of the brain and nervous system. They transmit information through electrical impulses and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. The brain contains billions of interconnected neurons, forming complex networks.
Synapses: Synapses are junctions between neurons where electrical impulses are transmitted from one neuron to another. This is where communication between neurons occurs, allowing for information processing, learning, and memory formation.
Cerebellum: The cerebellum, located at the base of the brain, is responsible for coordination, balance, and fine motor control. It plays a crucial role in movement and motor learning.
Brainstem: The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls basic life-sustaining functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. It includes the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain.
Sensory Processing: The brain receives and processes information from the five senses (sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch) to create our perception of the world.
Motor Control: The brain controls voluntary and involuntary movements of the body, from simple reflexes to complex actions. Motor areas in the cerebral cortex and the basal ganglia play crucial roles in motor control.
Memory and Learning: The brain is responsible for memory formation, storage, and retrieval. Different types of memory, including short-term and long-term memory, are associated with various brain regions.
Emotion and Behavior: The brain regulates emotions and behaviors through structures like the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Emotional processing and regulation are essential for social interactions and decision-making.
Consciousness: The brain is responsible for consciousness, our subjective awareness of the world and ourselves. The neural basis of consciousness remains a topic of ongoing scientific inquiry.
Plasticity: The brain exhibits neuroplasticity, which means it can reorganize and adapt to changing conditions. This capacity for change allows for learning, recovery from injury, and adaptation to new experiences.
Disorders and Diseases: Numerous neurological disorders and diseases can affect brain function, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, and traumatic brain injuries.
Understanding the brain's structure and functions is a central focus of neuroscience, a field that continually advances our knowledge of the brain and its role in cognition, behavior, and overall human functioning.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *